Water Resources
Our Approach
Water is an indispensable resource for the SUBARU Group’s business activities. Water is also an important resource for SUBARU customers who love and enjoy coexisting with nature. The risk of droughts, floods, and other disasters is increasing, however, due to climate change, while global population growth and economic development are increasing demand for water and raising the risk of water shortages and pollution.
To help alleviate these risks, the SUBARU Group is committed to the proper management of water consumption, as well as to minimizing the environmental impact of its discharged water. We are also actively engaging in activities to conserve forests that have a water storage function.
Management System
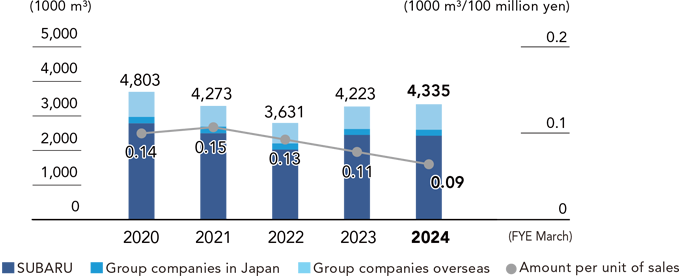
The Production & Environment Subcommittee manages the SUBARU Group’s water usage at each site, and both the total amount and amount used per unit of sales are maintained at a constant level.
The share of each water source in the total water consumption of the SUBARU Group, which consists exclusively of fresh water, is as follows: industrial water 65%, tap water 30%, and groundwater 6%. As we are well aware of the risks involved in using this valuable resource, we carefully monitor water consumption by conducting water risk assessments at major locations. Although the current assessment results show that the water risk is not high, we will continue to regularly assess our water risk levels and work to reduce water consumption in order to ensure a continuous water supply.
Risk Management
The SUBARU Group uses a third-party expert to implement water risk assessments* to ensure the sustainable use of water. These assessments estimated, among other things, the water supply and demand risk in the river basins in which the production bases are located, the probability of water-related disasters occurring, and the impact on public health and ecosystems on a five-point scale. Risk assessments utilized the most severe RCP8.5 climate change scenario adopted by the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC). These assessments showed that water risk at the Gunma Plant, Utsunomiya Plant, and Subaru of Indiana Automotive, Inc. is generally evaluated as moderate or lower. In FYE March 2024, we conducted an in-house water risk assessment using the World Resources Institute (WRI) Aqueduct Water Risk Atlas and WWF-DEG Water Risk Filter, confirming that water risk is generally below moderate, consistent with past surveys.
In addition, the SUBARU Group carries out disaster risk response for its business partners in Japan. When organizing the system for restoration support activities in the event of a contingency at our suppliers, we have also introduced a system to share information on disaster risks to both parties. Furthermore, for business partners near the Gunma Plant, a major plant receiving supplier materials at the SUBARU Group, we assess the risk of water-related disasters at more than 1,200 sites, including Tier 2 sites, and check contingency actions using a sheet for checking BCP initiative status as well as conduct mock drills and confirm subsequent corrective measures.
Gunma Plant and Subaru of Indiana Automotive, Inc.
According to an assessment in FYE March 2017, the water supply and demand risk at the Gunma Plant and Subaru of Indiana Automotive, Inc., both of which are automobile manufacturing bases, is moderate. It is expected that the current risk level will be maintained for the medium to long term, even when the impact of climate change is taken into account. No biodiversity conservation areas are identified at the lower reaches of the rivers. The vulnerability to water pollution is low.
Utsunomiya Plant
According to an assessment in FYE March 2018, the water supply and demand risk at the Utsunomiya Plant, which is our base for aerospace manufacturing, is moderate. This risk level is expected to drop in the future as an increase in the river flow rate and decrease in water demand are likely to take place. The plant is not located in an area at high risk of flood inundation or landslides. No biodiversity conservation areas or habitats for rare aquatic life are identified in the areas within 10 km downstream from the site. Going forward, we will continue to accurately monitor our water risk based on the assessments, ensure optimum water consumption in relation to local water demand, and help conserve the environment along the river.
- Reference databases:
- WRI Aqueduct Water Risk Atlas, WWF-DEG Water Risk Filter, PREVIEW Global Risk Data Platform, Climate Change Knowledge Portal, Integrated Biodiversity Assessment Tool, National Land Numerical Information: Possible Inundation Area Data and Sediment Disaster Hazard Area Data (Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism), NCD-VfU-GIZ Water Scarcity Valuation Tool (Version 1.0), Costing Nature/Water World, (Only for Gunma Plant and Utsunomiya Plant)
Business Partners
For business partners near the Gunma Plant, a major plant receiving supplier materials at the SUBARU Group, we assessed the risk of water-related disasters at more than 1,200 sites, including Tier 2 sites. As a result, about 40% of the sites were assessed as being at risk of flood inundation and landslides. The sites were identified as those that were exposed to a life-threatening inundation risk, those that were located in areas where restoration efforts would be extremely difficult, and those that were located in areas where there was a risk of mudslides and other landslides. In addition to sharing the results of these risk assessments, we work with business partners to check contingency actions using a sheet for checking BCP initiative status as well as conduct mock drills and confirm subsequent corrective measures.
Response to Water Risks:
Initiative
Site Initiatives
The total amount used is monitored and compiled for each location, and reported and verified at biannual meetings. Necessary measures are then taken as appropriate.
Water Consumption
Scope
- SUBARU:
- Gunma Plant, Tokyo Office, Utsunomiya Plant, Handa Plant, Handa West Plant, Ebisu Subaru Building, Accessory Center, SUBARU R&E Center (SKC), SUBARU R&E Center Bifuka Proving Ground, SUBARU Training Center
- Group companies in Japan:
- Yusoki Kogyo K.K., Fuji Machinery Co., Ltd., Ichitan Co., Ltd., Kiryu Industrial Co., Ltd., Subaru Logistics Co., Ltd., HBC Co.,Ltd.
- Group companies overseas:
- Subaru of Indiana Automotive, Inc., Subaru of America, Inc., Subaru Canada, Inc., Subaru Research & Development, Inc.
FYE March 2024 Water Consumption by Source (Thousands of m3)
| Scope | Tap Water | Industrial Water | Groundwater | Source of Water Intake |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Japan | 317 | 2,789 | 253 | Tone River, Watarase River |
| North America | 962 | 0 | 0 | Groundwater from the Teays Valley aquifer |
| Total | 1,279 | 2,789 | 253 |
Scope
- Japan:
- Gunma Plant, Tokyo Office, Utsunomiya Plant, Handa Plant, Handa West Plant, Yusoki Kogyo K.K., Fuji Machinery Co., Ltd., Ichitan Co., Ltd., Kiryu Industrial Co., Ltd., Subaru Logistics Co., Ltd., HBC Co.,Ltd.
- North America:
- Subaru of Indiana Automotive, Inc., Subaru of America, Inc., Subaru Canada, Inc., Subaru Research & Development, Inc.
Gunma Plant
In the Gunma region, wastewater from our plants is treated and then discharged into rivers after passing through an oil-water separation tank, where it eventually merges into the Tone River. Appropriate wastewater treatment is provided to ensure the water from the Tone River is safe during use for agricultural and domestic purposes in the downstream areas.
Utsunomiya Plant
The Utsunomiya Plant has introduced a surface treatment facility equipped with an ion-exchange water recycling system that converts wastewater into pure water. In FYE March 2024, 34,545 m3 (35.2%) of the total of 98,032 m3 of water used in the surface treatment facility was recycled and utilized at the plant as washing water for the facility.
Representative Surface Treatment Wastewater Processing and Recycling
In the Utsunomiya area, after treating wastewater from surface treatment processes we discharge it into the sewer system, and discharge rainwater and cooling water into the river after checking its quality in the final water quality monitoring tank. In addition, we dispose of wastewater from the painting process in the Handa area as industrial waste, and treat domestic wastewater in septic tanks prior to discharging it into Kinuura Port and the Agui River.
Utsunomiya Area Wastewater Treatment Process
Initiatives at Overseas Group Companies
Stormwater Management (Subaru of America, Inc.)
Subaru of America, Inc. (SOA) is addressing the risk of flooding on its premises by raising existing site grades by up to approximately 1.5 meters and planting wetland vegetation in areas with poor drainage, taking into account the importance of stormwater management. Its Subaru rain garden plays a role in mitigating the risk of flooding in the nearby Cooper River by temporarily storing stormwater.