Environmental Management
Our Approach
In its Environmental Policies, SUBARU states that our fields of business are “the earth, the sky and nature” and focuses on efforts aimed at coexistence with nature. The SUBARU Group will develop products that contribute to the environment through advanced technologies, and engage in environmental activities aimed at coexistence with nature. Furthermore, the Group has defined the Environment as one of our Six Priority Areas for Sustainability, and considers activities for the environment as key to the continuation of our business.
Within this area of the Environment, SUBARU has identified three issues to be prioritized: controlling climate change, realizing a circular economy, and coexistence with nature. By addressing these environmental issues, we aim to ultimately reduce the environmental impact on the natural world to virtually zero, and to go even further to make a positive impact.
In addition to the value of "Enjoyment and Peace of Mind" that we have provided so far, SUBARU is considering the use of sustainable materials to create new appeal, while promoting manufacturing reforms to reduce waste and engaging in sustainable "Monozukuri Innovation" and "Value Creation".
SUBARU Environmental Policies
SUBARU Environmental Philosophy
“The earth, the sky and nature” are SUBARU’s fields of business.
With the automotive and aerospace businesses as the pillars of SUBARU’s operations, our fields of business are the earth, the sky and nature.
Preservation of the ecosystem of our planet, the earth, the sky and nature, is of utmost importance to ensure the future sustainability of both society and SUBARU. We align our business strategy to enhance these global goals in all of our operations.
- We develop and deliver products to meet social needs and contribute to the environment through advanced technologies.
By striving to create advanced technologies that put the environment and safety first, we will develop and deliver products that can contribute to protecting the earth’s environment. - We focus on efforts aimed at coexistence with nature.
Together with efforts to reduce CO2 emissions in all of our operations, we will promote active engagement with nature by stressing forest conservation. - We take on challenges as one through an all-SUBARU approach.
Utilizing our unique organizational character that allows us to oversee the entire supply chain, all of us together will take on the challenges of environmental protection of our planet through an all-SUBARU approach.
Environmental Principles
SUBARU’s fields of business are the earth, the sky and nature. SUBARU understands that the health and preservation of biodiversity and controlling climate change are critical to ensuring a sustainable future for our planet earth, nature, communities, and businesses.
- Products:
- We develop our products and conduct R&D in light of the life cycle environmental impacts of our products.
- Purchasing:
- Our purchasing activities reflect consideration for biodiversity and other aspects of environmental protection.
- Production:
- We strive to minimize our environmental impact through improving energy efficiency and waste management.
- Logistics:
- We strive to minimize our environmental impact through enhancing energy efficiency and promoting pollution prevention.
- Sales:
- We endeavor to recycle resources efficiently and reduce waste.
- Management:
- We will strive to improve our sustainability program through contributions that meet social needs and by publicizing our activities as Team Subaru.
Management System
Environmental Management System
SUBARU comprehensively manages the entire progress and direction of its environmental management measures through the Environment Committee and based on the cross-company integrated environmental management system (EMS). Leveraging this structure, we promote various environmental management activities across the entire SUBARU Group, including formulating and achieving medium- to long-term environmental targets, ensuring compliance with environmental laws and regulations, managing chemical substances, and aggregating environmental performance data.
The Executive Officer in charge of the Sustainability Division appointed by the Board of Directors oversees the integrated EMS and chairs the Environment Committee. In principle, the related issues are reviewed regularly, at least once a year, and details of discussions held by the Environment Committee are reported to the Sustainability Committee. Important issues are discussed and reported at the Executive Management Board Meeting and by the Board of Directors.
In addition, four subcommittees have been created under the Environment Committee, with participation from major Group companies and comprising the SUBARU Group’s environmental management organization.
Environmental Risk Management System
SUBARU, in cooperation with relevant departments and staff involved with environmental laws and regulations at domestic Group companies, regularly identifies the environmental risks involved in its business activities (environmental accidents, pollution, noncompliance with laws and regulations, etc.) and fosters the management of the identified risks to prevent and minimize their materialization. We also standardize the procedures to be followed when detecting an environmental risk and conduct drills in ordinary times so that we can promptly implement response measures in case of emergency and then take measures to prevent the recurrence of similar accidents, while preventing the spread of environmental pollution.
Implementation of Environmental Audits
- Regular auditing based on the ISO 14001 environmental management system
- On-site contractors audits to ensure proper collection, transportation, and disposal of industrial waste
- On-site audits of compliance with environmental laws, regulations, and ordinances
Procedures to Be Followed in Case of an Environmental Accident
Acquisition of External Certification for EMS
SUBARU has been working to build an EMS, and its sites, suppliers, domestic and overseas consolidated production companies, and dealerships have had their EMS certified by external organizations
Major Certifications
ISO 14001
SUBARU CORPORATION and its six consolidated production and logistics subsidiaries in Japan and three consolidated production and sales subsidiaries in North America have obtained ISO 14001 certification for their EMS. With the start of operation of the Kitamoto Plant, this site has been added to the organizational scope as a site within the Gunma Plant.
ISO 50001*1
In 2012, Subaru of Indiana Automotive, Inc., which is our production base in North America, acquired certification for ISO 50001, which is the international standard for energy management systems (EnMS).
- *1
- International standard applicable to all organizations that sets the requirements to be met by business operators when conducting activities to build an energy management system, including the formulation of policies, targets, and plans for their energy use and the determination of management procedures.
Establishment of EMSs and EnMSs by the SUBARU Group
| Plants and offices | Dealerships | Business Partners | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Category | SUBARU CORPORATION | Domestic Consolidated Production and Logistics Companies | Overseas Consolidated Production Companies | Japan | Overseas | |
| Certification obtained for EMSs/EnMSs | ISO 14001 | ISO 14001 | ISO14001 ISO 50001 |
Eco Action 21*2 | ISO14001 | ISO 14001, Eco Action 21 or self-certification |
| Target | Gunma Plant Tokyo Office Utsunomiya Plant Head Office |
Fuji Machinery Co., Ltd.*3 Kiryu Industrial Co., Ltd.*3 Yusoki Kogyo K.K.*3 Subaru Logistics Co., Ltd.*3 FAS Corporation*3 Ichitan Co., Ltd. Six companies in total |
Subaru of Indiana Automotive, Inc. | SUBARU Dealerships 33 companies in total |
Subaru of America, Inc. Subaru Canada, Inc. Two companies in total |
Green procurement Suppliers of materials |
- *2
- Environmental conservation activity promotion program formulated by Japan’s Ministry of the Environment in which SMEs work on three themes: EMS, environmental measures, and environmental reporting.
- *3
- Group certification: SUBARU CORPORATION and its affiliated companies marked with an asterisk (*) carry out mutual internal audits on their EMSs within the scope required for ISO 14001 group certification.
EMS Established by Dealerships in Japan
All 33 consolidated dealerships and 10 non-consolidated dealerships in Japan have acquired Eco Action 21 certification. Under the certification system, they promote their EMS and carry out environmental audits on a regular basis for environmental conservation and compliance with environmental laws and regulations.
Moreover, we collect data on domestic dealerships’ energy use, CO2 emissions, waste generation, and water use through the SUBARU Group’s unique data system for environmental reporting. We use this data to reduce our environmental impact at these dealerships.
EMS Established by Retailers in the U.S.
(Subaru of America, Inc.)
Subaru of America, Inc. (SOA) promotes the Eco-Friendly Retailer Program that encourages SUBARU retailers in the U.S. to reduce energy consumption, water usage, waste and other environmental impacts. To be certified under the Eco-Friendly Retailer Program, a company must meet the established standards in areas such as energy efficiency and recycling. As of 2023, 255 retailers, or 40%, are participating in the program.
Management of Chemical Substances
In order to minimize the impact of chemical substances used in automobiles on people and to help preserve the environment through reduced impact, there is a growing international movement to require the identification, appropriate management and handling, and information disclosure of chemical substances contained in products.
SUBARU uses IMDS*1 as a method to manage its entire supply chain in order to identify which chemical substances are used in what amount in each of the several tens of thousands of parts that comprise its automobiles. Furthermore, we use SUBARU’s proprietary CSMS*2 to substitute and/or manage elimination of substances prohibited under laws and regulations such as the REACH regulation*3, the ELV Directive*4, the U.S. Toxic Substances Control Act, and Japan's Chemical Substance Control Law, and to appropriately disclose information on controlled substances required by the Waste Framework Directive (WFD*5) and other regulations.
This work to manage chemical substances also aids in the SUBARU Group’s work toward resource and other recycling.
- *1
- IMDS: International Material Data System, an international materials database for the automobile industry
- *2
- CSMS: Chemical Substance Management System
- *3
- REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals) Regulation: A European regulation requiring all chemical substances to be subject to management or restriction measures commensurate to the risk that they pose to humans and the environment.
- *4
- ELV (End-of-Life Vehicles) Directive: A European automotive disposal directive requiring reduction of environmental impact from vehicles that are no longer used.
- *5
- WFD (Waste Framework Directive): Requires waste control and management.
International Material Data System
Management of Chemical Substances through the IMDS

Targets and Results
Environment Action Plan 2030 and Other Key Environmental Initiatives
SUBARU has established its medium-term environmental plan, divided between the Environmental Action Plan 2030 and other key environmental initiatives, depending on the characteristics of each environmental issue. Within our environmental plans, 2050 is considered to be the long term horizon, while 2030 is the medium term horizon.
Environment Action Plan 2030:
This is a Group-wide plan with a medium- to long-term perspective and initiatives that spiral upward to address future expectations.
Other key environmental initiatives:
These granular initiatives are from a short- to medium-term perspective and are designed to meet current expectations.
The two main features of Environment Action Plan 2030 are milestone goals to achieve by 2050 and moving targets that change according to the expectations of society.
Through initiatives based on the new environmental plan, SUBARU will sincerely address the expectations of current and future generations and further contribute to the realization of a sustainable society.
Key Initiatives of Environment Action Plan 2030
Climate Change
I. Key Initiatives of Environment Action Plan 2030
| Field | Long-Term Vision | Environment Action Plan 2030 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Medium-Term Goals (Primary Category) | Short-Term Initiatives (1–3 Years) | Major Results in FYE March 2024 | |||||
| Bases | Goals by Base | Components of Primary Initiatives | |||||
| Scope 1 and 2 (plants and offices) | Target carbon neutrality by FYE March 2051. | Reduce CO2 emissions by 60% in FYE March 2036 compared with FYE March 2017 (total volume basis) | Plants | Reduce CO2 emissions from plants in Japan. | Reduce CO2 emissions by 60% in FYE March 2036 compared with FYE March 2017 (total volume basis) |
|
|
|
|
||||||
| Reduce CO2 emissions from plants overseas. |
|
|
|||||
| Head Office | Reduce CO2 emissions from the Head Office building*3. | Reduce CO2 emissions to zero. |
|
|
|||
| Dealership | Reduce CO2 emissions from dealerships in Japan. | Aggregate information and upgrade systems to reduce CO2 emissions. |
|
|
|||
| Scope 3 (products) | On a well-to-wheel*5 basis, we will pursue our goal of reducing the average CO2 emissions from new vehicles (in operation) sold worldwide by at least 90% by 2050, compared with 2010*6. |
|
Automobiles | Improve fuel economy and equip vehicles with electrification technology. |
|
|
|
| Clean energy use. |
|
|
|
||||
| Road traffic improvement – IT technology (Self-driving technology and preventive safety technology). | Develop driving assistance technology and preventive safety technology centered on the EyeSight Advanced Driver Assistance System and expand into more markets. |
|
|
||||
- *1
- Gunma Plant, Tokyo Office, Utsunomiya Plant/dd>
- *2
- Fuji Machinery Co., Ltd., Ichitan Co., Ltd., Kiryu Industrial Co., Ltd., Subaru Logistics Co., Ltd., Yusoki Kogyo K.K.
- *3
- Subaru of Indiana Automotive, Inc.
- *4
- Head Office floors of the Ebisu Subaru Building (Shibuya-ku, Tokyo)
- *5
- Well-to-Wheel: Approach to calculating CO2 emissions including the emissions produced by the generation of electricity to be used by EVs and other vehicles.
- *6
- Reduce total CO2 emissions calculated based on the fuel efficiency (notified value) of all SUBARU automobiles sold across the world by 90% or more relative to the 2010 levels in 2050. Changes in the sales quantity due to changes in the market environment shall be taken into consideration, while minor changes in running distance shall not.
- *7
- Refers to the technology used to foster the use of electricity for EVs, HEVs, and others.
- *8
- Excluding models that receive OEM supply from other companies.
II. Other key environmental initiatives
| Field | Item | Short-Term Initiatives (1–3 Years) | Major Results in FYE March 2024 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Logistics | Implement measures to reduce CO2 in line with the Energy Saving Law. | Reduce CO2 emission intensity by 1% every year, using FYE March 2007 as a benchmark. |
|
Resource Recycling
I. Key Initiatives of Environment Action Plan 2030
| Field | Long-Term Vision | Environment Action Plan 2030 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Medium-Term Goals | Short-Term Initiatives (1–3 Years) | Major Results in FYE March 2024 | ||
| Components of Primary Initiatives | ||||
| Products (Automobiles) | Contribute to resource recycling and carbon neutrality. |
|
|
|
| Production | Help create a recycling-oriented society with clean production plants. | Achieve zero emissions at production plants*4 in Japan and overseas (zero landfill waste either directly or indirectly). | Maintain zero emissions at production plants in Japan and overseas (zero landfill waste either directly or indirectly). | Maintain zero emissions at production plants in Japan and overseas. As part of a recycling initiative for waste plastic, improved the thermal recycling rate by separating and discharging raw materials for alternative fuel (refuse paper and plastic fuel, or RPF) from simple incineration waste. |
|
||||
| Appropriately manage water use at both domestic and overseas production plants*4. | Maintain zero emissions at production plants in Japan and overseas (zero landfill waste either directly or indirectly). | Manage actual amount of water, report and verify at biannual meetings, and implement necessary measures as appropriate. | ||
| Improve the wastewater treatment process through the updating of chemical management pumps and chemical dosing program. | ||||
- *1
- Including material and chemical recycling.
- *2
- Excluding models supplied by OEMs.
- *3
- Materials and suppliers with lower CO2 emissions and environmental pollution at the manufacturing stage.
- *4
- Parent company: Gunma Plant, Tokyo Office, Utsunomiya Plant; Subsidiaries: Fuji Machinery Co., Ltd., Kiryu Industrial Co., Ltd., Ichitan Co., Ltd., Subaru Logistics Co., Ltd., Yusoki Kogyo K.K., Subaru of Indiana Automotive, Inc.
II. Other key environmental initiatives
| Field | Item | Short-Term Initiatives (1–3 Years) | Major Results in FYE March 2024 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Products (Automobiles) | Recyclability improvement |
|
|
| Promotion of life-cycle assessment | Promote disclosure of life-cycle assessment (LCA) data. |
|
|
| Production | Waste control and proper disposal | Continue to control waste generation through means such as improving yield and packing style, and properly dispose of waste. |
|
Pollution Prevention and Reduction of Hazardous Chemical Use
I. Key Initiatives of Environment Action Plan 2030
| Field | Long-Term Vision | Environment Action Plan 2030 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Medium-Term Goals | Short-Term Initiatives (1–3 Years) | Major Results in FYE March 2024 | ||
| Components of Primary Initiatives | ||||
| Production | Coexist with communities with production plants that are socially and environmentally responsible. | Target zero serious environmental accidents*. |
|
|
- *
- Zero emissions into the environment, accidents, complaints, or violations of statutory standards.
II. Other key environmental initiatives
| Field | Item | Short-Term Initiatives (1–3 Years) | Major Results in FYE March 2024 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Components of Primary Initiatives | |||
| Products (Automobiles) | Promote the introduction of low-emission vehicles to improve air quality. |
|
Develop vehicles compliant with particle number (PN) regulations. |
|
|
||
| Promote the management and reduction in the use of environmentally hazardous substances. |
|
|
|
|
|
||
| Production | Further reduce per unit of volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions (g/m2) at production lines. |
|
|
| Continue to reduce emissions of Pollutant Release and Transfer Register (PRTR) substances into the environment. |
|
|
Disclosure and Discussion of Coexistence with Communities and Environmental Information
Key Initiatives of Environment Action Plan 2030
| Field | Medium-Term Goals | Contact point | Environment Action Plan 2030 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Short-Term Initiatives (1–3 Years) | Major Results in FYE March 2024 | |||
| Components of Primary Initiatives | ||||
| Management | Earn greater trust from society through environmental information disclosure and dialogue. | Investor Relations Department |
|
|
Collaborate with Customers and Promote Environmental Management
Other key environmental initiatives:
| Field | Item | Contact point | Short-Term Initiatives (1–3 Years) | Major Results in FYE March 2024 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Procurement | Request suppliers in Japan and overseas to build, maintain, and strengthen an EMS. | Purchasing Committee |
|
|
|
|
|||
| Reduce environmentally hazardous substances. |
|
|
||
| Apply the SUBARU Supplier CSR Guidelines and Green Procurement Guidelines. |
|
|
||
| Sales (Automobiles) | Provide support to SUBARU dealerships’ environmental activities. | Sales and Service Environment Subcommittee |
|
|
|
||||
| Management | Operate and upgrade EMS. | Sustainability Promotion Department |
|
|
|
|
- *
- Environmental conservation activity promotion program formulated by Japan’s Ministry of the Environment in which SMEs work on three themes: EMS, environmental measures, and environmental reporting.
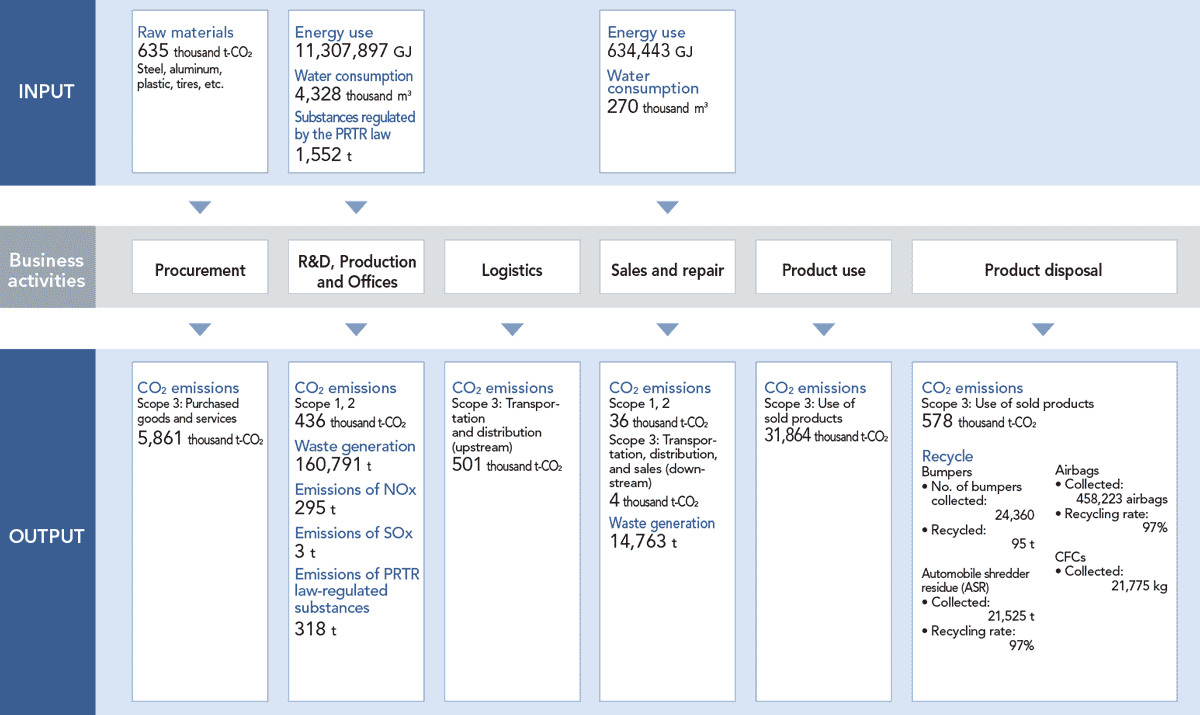
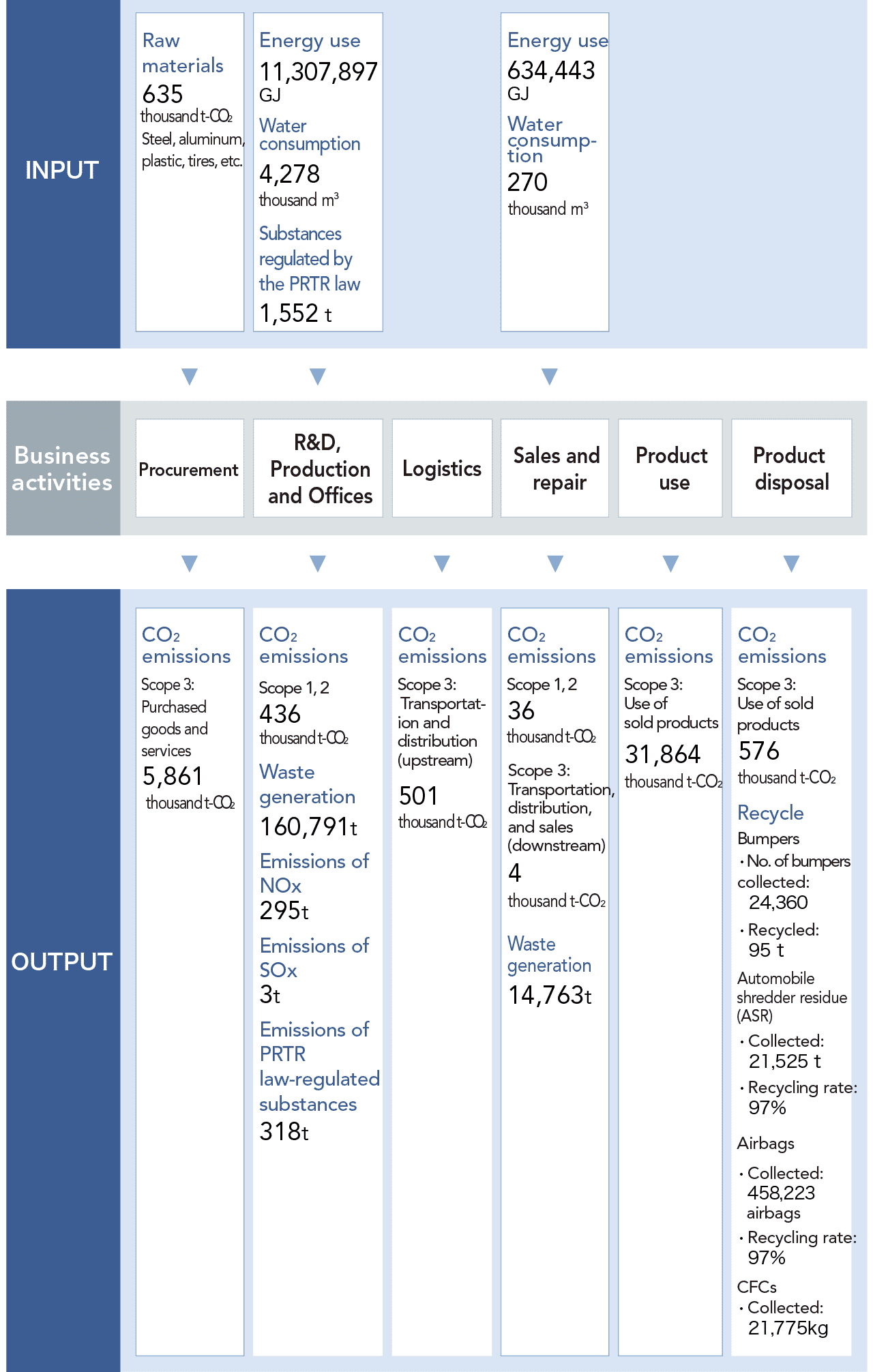
SUBARU Group Material Flow
Scope
- [Procurement]
- SUBARU: Gunma Plant, Utsunomiya Plant, Handa Plant, Handa West Plant
- [R&D and production]
- SUBARU: Gunma Plant, Utsunomiya Plant, Handa Plant, Handa West Plant, Tokyo Office, Ebisu Subaru Building, Accessory Center, Subaru Research and Experiment Center, Subaru Test & Development Center Bifuka Proving Ground, SUBARU Training Center, Omiya Subaru Building
Domestic Group companies: 19 domestic consolidated subsidiaries
Overseas Group companies: Subaru of Indiana Automotive, Inc., North American Subaru, Inc., Subaru Research & Development, Inc.
- [Logistics]
- Land transport (in Japan) and marine transport
- [Sales and repair]
- 33 dealerships that are consolidated subsidiaries, Subaru of America, Inc. and Subaru Canada, Inc.
- [Product use and disposal]
- Sold SUBARU vehicles
Environmental Investment
Calculation Method
SUBARU has its own guidelines for calculating and tabulating the amount of environmental investments made by the Company. These guidelines are aligned with SUBARU’s environmental conservation organization.
Calculation Results
Environmental investment in FYE March 2024 decreased 430 million yen year on year to 2,541 million yen.
SUBARU Group Environmental Investment
(Millions of yen)
| Item | Category | Consolidated | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FYE March 2022 | FYE March 2023 | FYE March 2024 | ||
| (1) Cost in the business area | (i) Pollution prevention cost | 259 | 797 | 999 |
| (ii) Global environment conservation cost | 155 | 648 | 455 | |
| (iii) Resource recycling cost | 7 | 0 | 5 | |
| (2) R&D cost | R&D cost to reduce environmental impact | 2,849 | 1,526 | 1,082 |
| (3) Environmental remediation costs | Costs for remediating soil and groundwater pollution | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Grand total | 3,271 | 2,970 | 2,541 | |
- Note:
- Due to rounding, the sum may not exactly match the corresponding total.
Scope
- SUBARU:
- SUBARU CORPORATION
- Domestic Group companies:
- Yusoki Kogyo K.K., Fuji Machinery Co., Ltd., Ichitan Co., Ltd., Kiryu Industrial Co., Ltd., Subaru Logistics Co., Ltd.
- Overseas Group companies:
- Subaru of Indiana Automotive, Inc., Subaru of America, Inc., Subaru Canada, Inc., Subaru Research & Development, Inc.
Environmental Education
SUBARU deems it important for employees to conduct business and environmental activities with a strong awareness of environmental issues and the importance of environmental efficiency. Based on this recognition, we provide employees with a range of environmental education according to rank and job type.
New Employee Training
This program covered topics such as the SUBARU Group’s Six Priority Areas for Sustainability to become a sustainable company and the SUBARU Global Sustainability Policy.
Training on Environmental Laws and Regulations
SUBARU provides training on environmental laws and regulations as necessary to ensure compliance with such laws and regulations. Based on the results of a questionnaire conducted after the training in FYE March 2023, we did not conduct training on environmental laws and regulations in FYE March 2024, but held training on measures to reduce Scope 1 and 2 emissions. In FYE March 2025, we intend to hold training sessions on the topic of waste management. We will continue to reference questionnaires and issues related to environmental laws and regulations as we strive to provide training in accordance with internal needs.
ISO 14001 New Internal Auditors Training Seminar
We also held the ISO 14001 New Internal Auditors Training Seminar, taught by external lecturers in an online format, to enhance the internal auditing system for our ISO 14001-certified EMS and to strengthen environmental conservation activities conducted at our workplaces. In FYE March 2024, the 166 participants worked hard to gain the knowledge required of internal auditors.
Dealerships in Japan
In FYE March 2024, a total of 605 people participated in training on environmental laws and regulations, targeting dealership head office managers and personnel, and workshops to help dealerships acquire industrial waste management licensing for practical personnel at dealership head offices and locations. In addition, we are developing materials as necessary regarding amendments made to laws and regulations. Through these efforts, we are deepening understanding of environmental laws and regulations at our dealerships in Japan.
Subaru Logistics Co., Ltd.
Subaru Logistics Co., Ltd. conducts in-house training on environmental laws and regulations in order to ensure compliance with environmental laws and regulations. In FYE March 2024, we held web-based training for all employees on our environmental initiatives in conjunction with Environment Month (June 2023) as designated by the Japanese government. This training is part of our efforts to raise awareness among employees about our environmental initiatives.